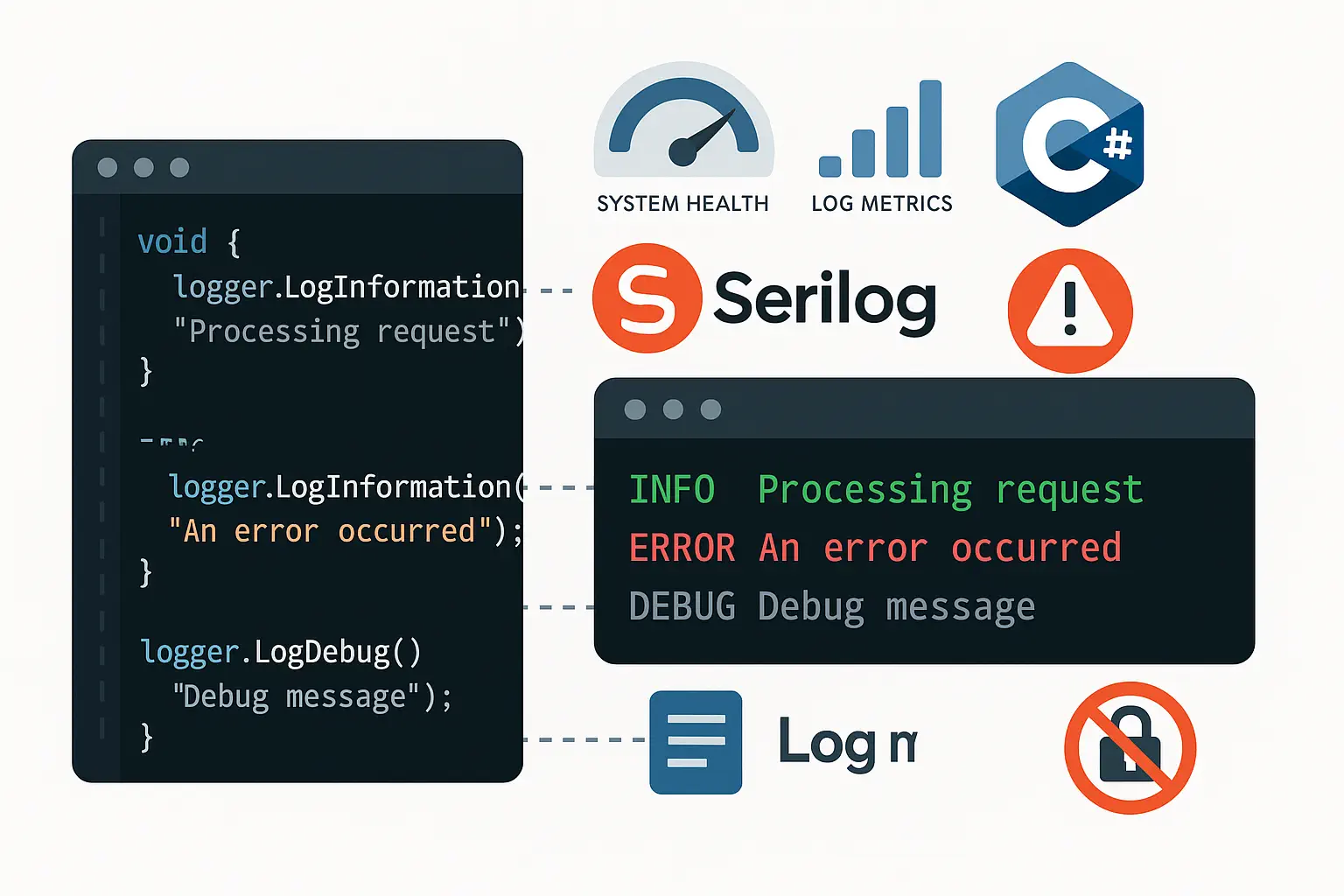
Why Logging Matters
Effective logging is essential for debugging, monitoring, and auditing. It helps uncover issues in production and ensures traceability of actions in your applications.
What Makes a Good Log Message
// Good
_log.Info("User login successful: userId=1234");
// Bad
_log.Info("Something happened");
Log Levels Explained
| Level | Purpose | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| DEBUG | Internal dev info | Tracing logic, flow |
| INFO | High-level events | User login, request received |
| WARN | Unexpected but non-breaking | Retry attempt, fallback used |
| ERROR | Application failure | DB not reachable, exception thrown |
| FATAL | System critical failure | Service crash |
Structured vs Unstructured Logging
// Structured
{
"timestamp": "2025-06-09T08:00:00Z",
"level": "INFO",
"message": "User logged in",
"userId": "1234"
}
// Unstructured
User logged in successfully with ID 1234
Logging in C# with Serilog
Log.Logger = new LoggerConfiguration()
.MinimumLevel.Debug()
.WriteTo.Console()
.WriteTo.File("logs/log.txt", rollingInterval: RollingInterval.Day)
.CreateLogger();
Log.Information("Application Started");
Logging in Python
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO,
format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
logging.info("Service started")
Real-World Logging Examples
// C# Bad
_log.Error("Exception occurred");
// C# Good
_log.Error(ex, "Payment processing failed for OrderId={OrderId}", orderId);
# Python Bad
logging.warning("Something is wrong")
# Python Good
logging.warning("Payment delay detected for user_id=%s", user_id)
Anti-Patterns to Avoid
- ❌ Logging passwords, tokens, or PII
- ❌ Logging stack traces without context
- ❌ Overusing INFO/ERROR for all logs
- ❌ Ignoring structured logs in favor of raw text
Stay tuned for quiz and downloadable guide!