🔐 Introduction
Authentication is the foundation of application security. As we build modern applications that connect with APIs, third-party services, and mobile clients, ensuring proper identity verification becomes critical. Misconfigured authentication can expose user data, leak credentials, and open doors for unauthorized access.
🔍 Authentication vs Authorization
Many developers confuse authentication and authorization. Authentication confirms the user is who they say they are. Authorization defines what the authenticated user is allowed to do within the system. Mistaking one for the other can lead to privilege escalation vulnerabilities.

❌ Insecure Example
// No role-based check
[Authorize]
public IActionResult SecureData() => Ok("Everyone with token can see this");✅ Secure Example
[Authorize(Roles = "Admin")]
public IActionResult SecureData() => Ok("Only admins can see this");🔑 OAuth2 Explained
OAuth2 is an open standard for access delegation, commonly used for token-based authorization. It enables applications to access user data without sharing credentials, using flows like Authorization Code or Client Credentials. Misusing OAuth2 can expose tokens or allow impersonation.
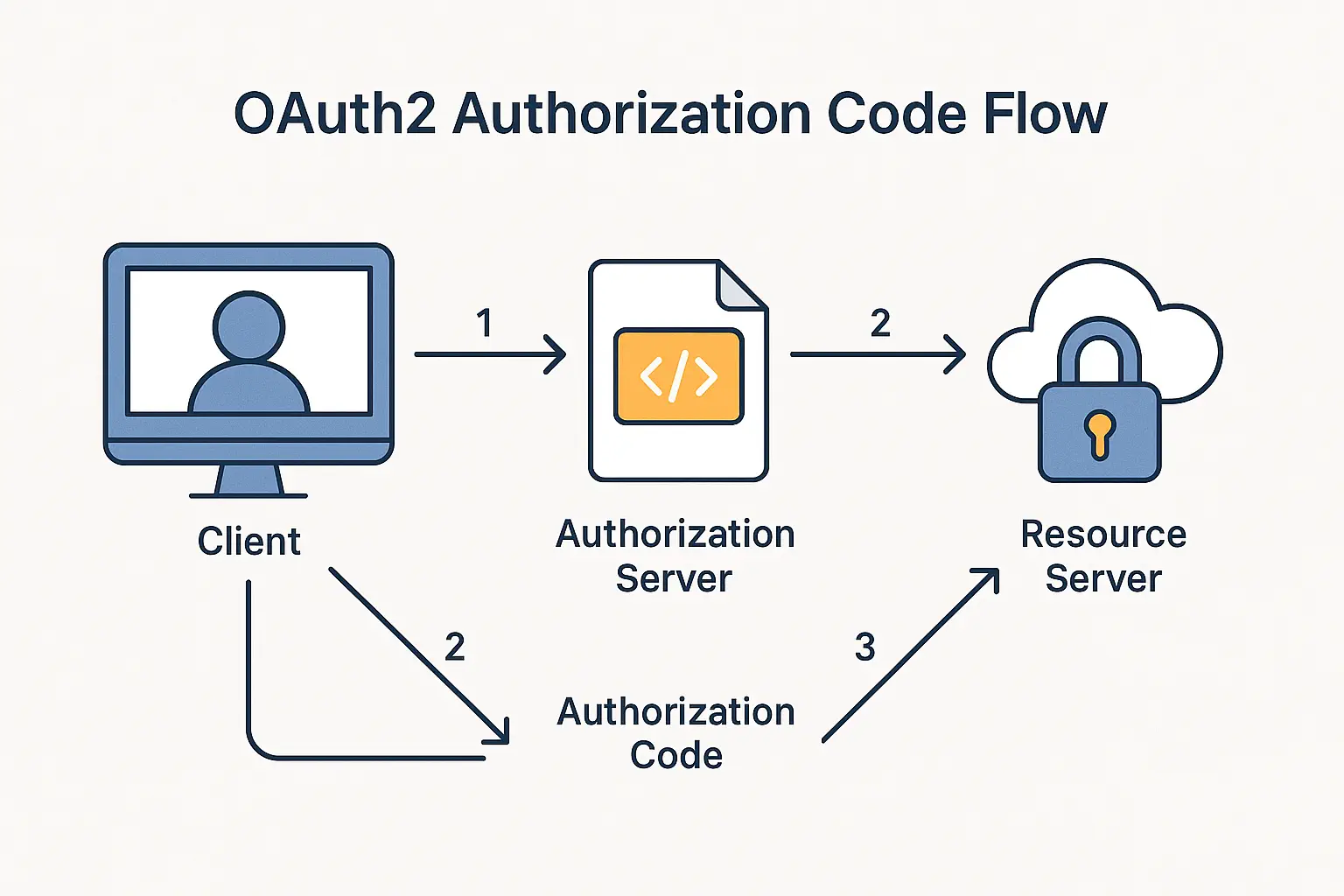
❌ Insecure Example
// Using hardcoded token and no OAuth flow
httpClient.DefaultRequestHeaders.Add("Authorization", "Bearer static_token");✅ Secure Example
services.AddAuthentication(options =>
{
options.DefaultScheme = "Cookies";
options.DefaultChallengeScheme = "OAuthProvider";
})
.AddCookie("Cookies")
.AddOAuth("OAuthProvider", options =>
{
options.ClientId = Configuration["OAuth:ClientId"];
options.ClientSecret = Configuration["OAuth:ClientSecret"];
options.CallbackPath = new PathString("/signin-oauth");
options.AuthorizationEndpoint = "https://provider.com/oauth/authorize";
options.TokenEndpoint = "https://provider.com/oauth/token";
options.SaveTokens = true;
});🗾 OpenID Connect
OpenID Connect (OIDC) extends OAuth2 to add identity verification using ID tokens. These tokens help applications confirm the user's identity in a standardized, secure manner. If implemented incorrectly, malicious tokens could be accepted without validation.
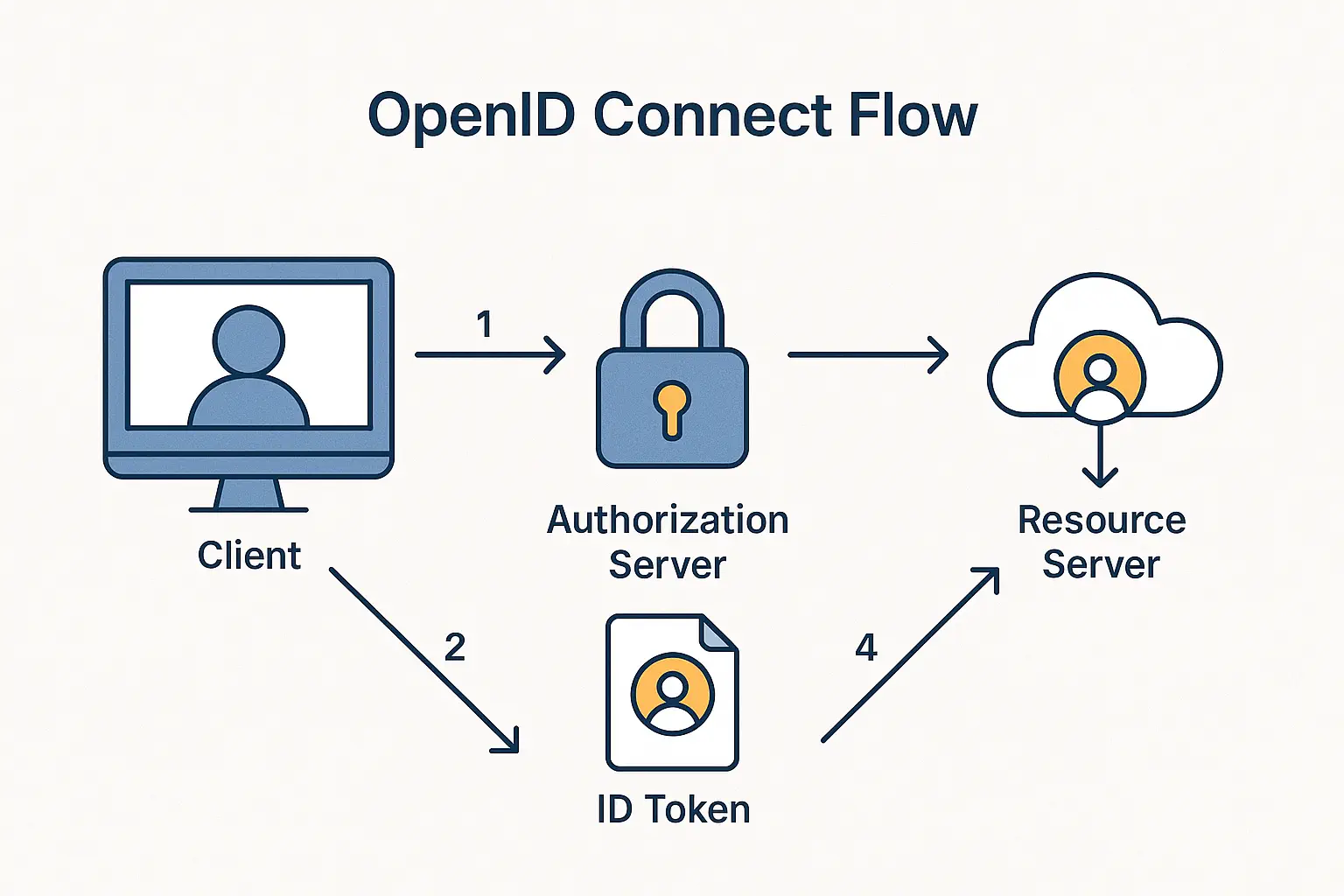
❌ Insecure Example
// Just trusting any ID token without validating claims
var idToken = context.Request.Headers["Authorization"].ToString().Replace("Bearer ", "");
var payload = JWT.Decode(idToken); // Without validation✅ Secure Example
services.AddAuthentication(options =>
{
options.DefaultScheme = "Cookies";
options.DefaultChallengeScheme = "oidc";
})
.AddCookie()
.AddOpenIdConnect("oidc", options =>
{
options.Authority = "https://login.example.com";
options.ClientId = "client_id";
options.ClientSecret = "secret";
options.ResponseType = "code";
options.SaveTokens = true;
options.Scope.Add("openid");
options.Scope.Add("profile");
});🔐 JSON Web Tokens (JWTs)
JWTs are compact, URL-safe tokens used to securely transmit information. They enable stateless authentication across microservices and APIs. JWTs must be properly signed and validated to avoid forgery or replay attacks.
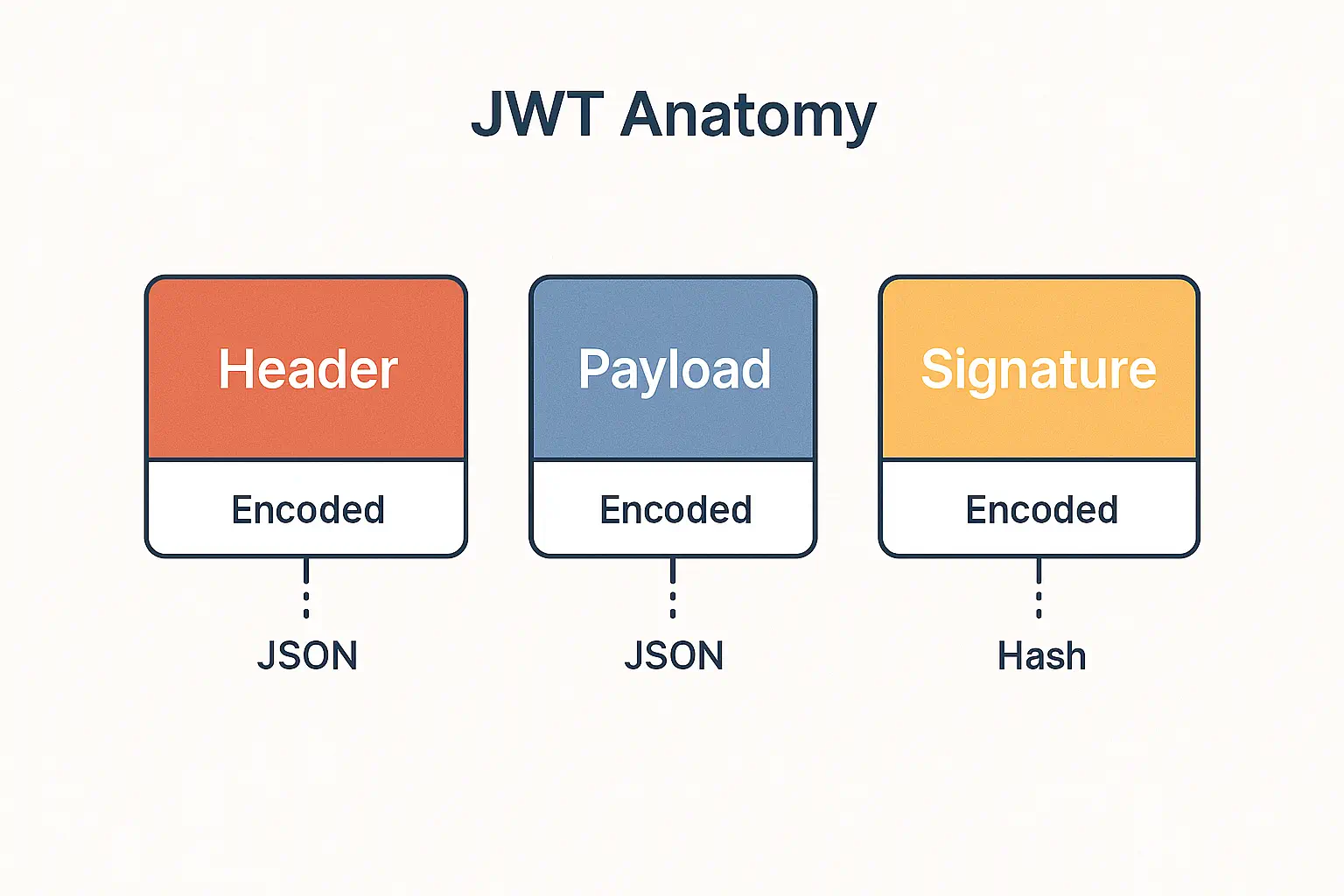
❌ Insecure Example
// WARNING: This is NOT secure
services.AddAuthentication("Bearer")
.AddJwtBearer("Bearer", options =>
{
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
ValidateIssuer = false,
ValidateAudience = false,
ValidateLifetime = false,
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = false
};
});✅ Secure Example
services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
options.Authority = "https://login.example.com";
options.Audience = "api1";
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
ValidateIssuer = true,
ValidateAudience = true,
ValidateLifetime = true,
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true
};
});⚠️ Common Implementation Mistakes
Even when using secure technologies, improper implementation can result in serious vulnerabilities. Avoid these common pitfalls:

- Storing tokens in localStorage
- Using HS256 for public clients
- Mixing ID and Access tokens
❌ Insecure Example
// Using localStorage to store access token in JS app
localStorage.setItem("token", accessToken);✅ Secure Example
services.ConfigureApplicationCookie(options =>
{
options.Cookie.HttpOnly = true;
options.Cookie.SecurePolicy = CookieSecurePolicy.Always;
options.Cookie.SameSite = SameSiteMode.Strict;
});🧰 Best Practices Checklist
Follow these best practices when implementing secure authentication:

- ✅ Use HTTPS -
app.UseHttpsRedirection(); - 🔄 Rotate secrets - Use DataProtection APIs
- ⏰ Short-lived tokens - Configure token lifespan
- 🧪 Input validation - Always validate headers and claims
🧑💻 Real-World Login Flow
A minimal secure login implementation using JWT or OIDC, enabling authenticated access to protected routes.
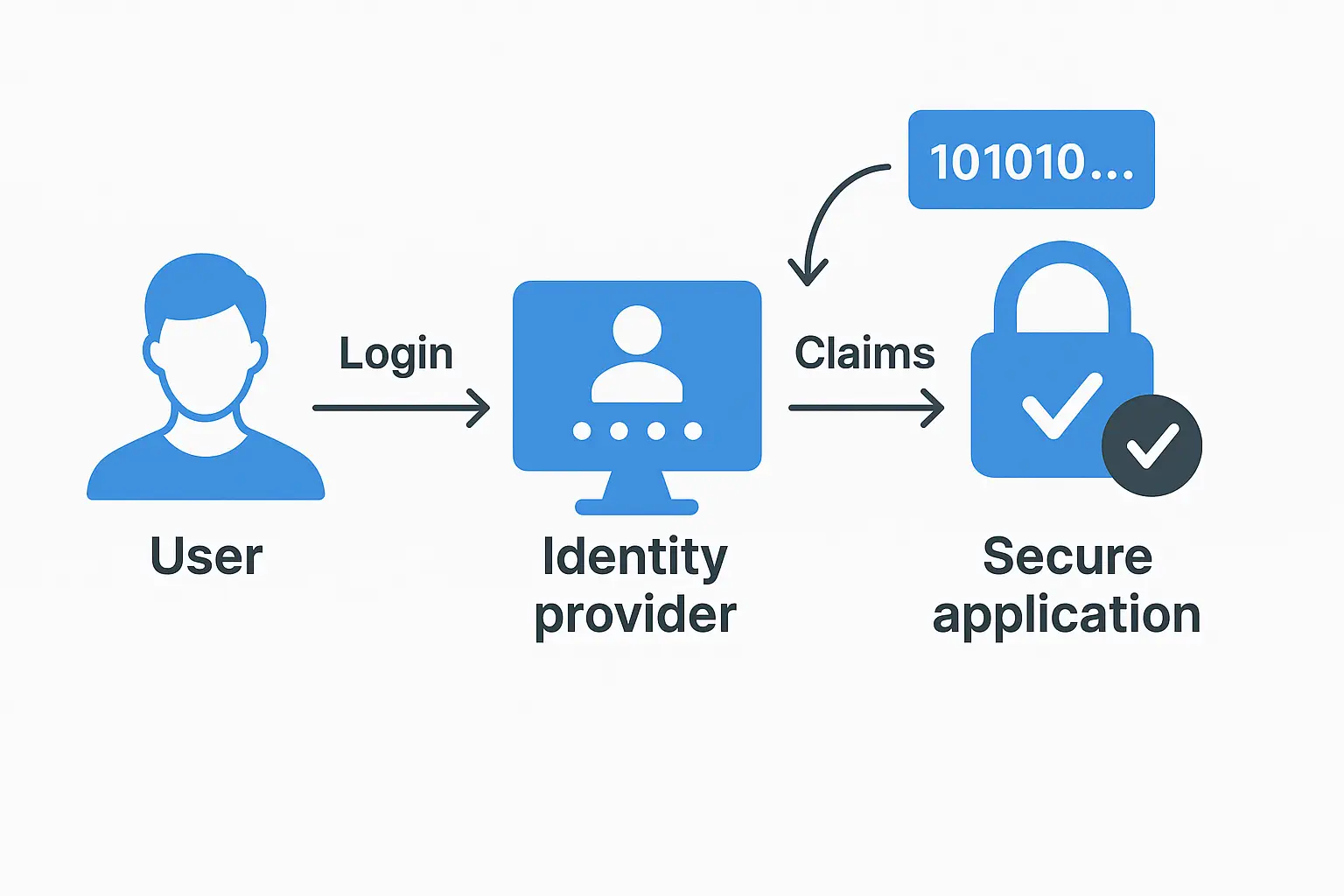
✅ Secure Example
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapGet("/profile", [Authorize] (ClaimsPrincipal user) =>
{
return Results.Json(new { Name = user.Identity.Name });
});📄 Real-World Breaches
High-profile breaches underscore the importance of getting authentication right:
- Facebook (2018): Access tokens leaked via “View As” feature. Lesson: Minimize token scope and lifetime.
- Uber (2016): Tokens in GitHub repo were stolen. Lesson: Secure secrets properly.
- Slack (2022): Long-lived token reused. Lesson: Always use refresh tokens and short expiry.
🔗 Conclusion
Secure authentication is no longer optional. Implement OAuth2 for authorization, OpenID Connect for identity, and JWTs for stateless tokens — but do it right. The smallest misconfiguration can lead to major breaches.
Explore more: OWASP A01 - Broken Access Control