Introduction
The Strategy Pattern is designed to encapsulate a family of algorithms and make them interchangeable at runtime. It enables the algorithm to vary independently from the clients that use it.
What is the Strategy Pattern?
Definition: Defines a family of algorithms, encapsulates each one, and makes them interchangeable.
- Category: Behavioral
- Also Known As: Policy Pattern
Real-World Analogy
A navigation app that offers routes for walking, driving, and transit—each a separate strategy, selected at runtime.
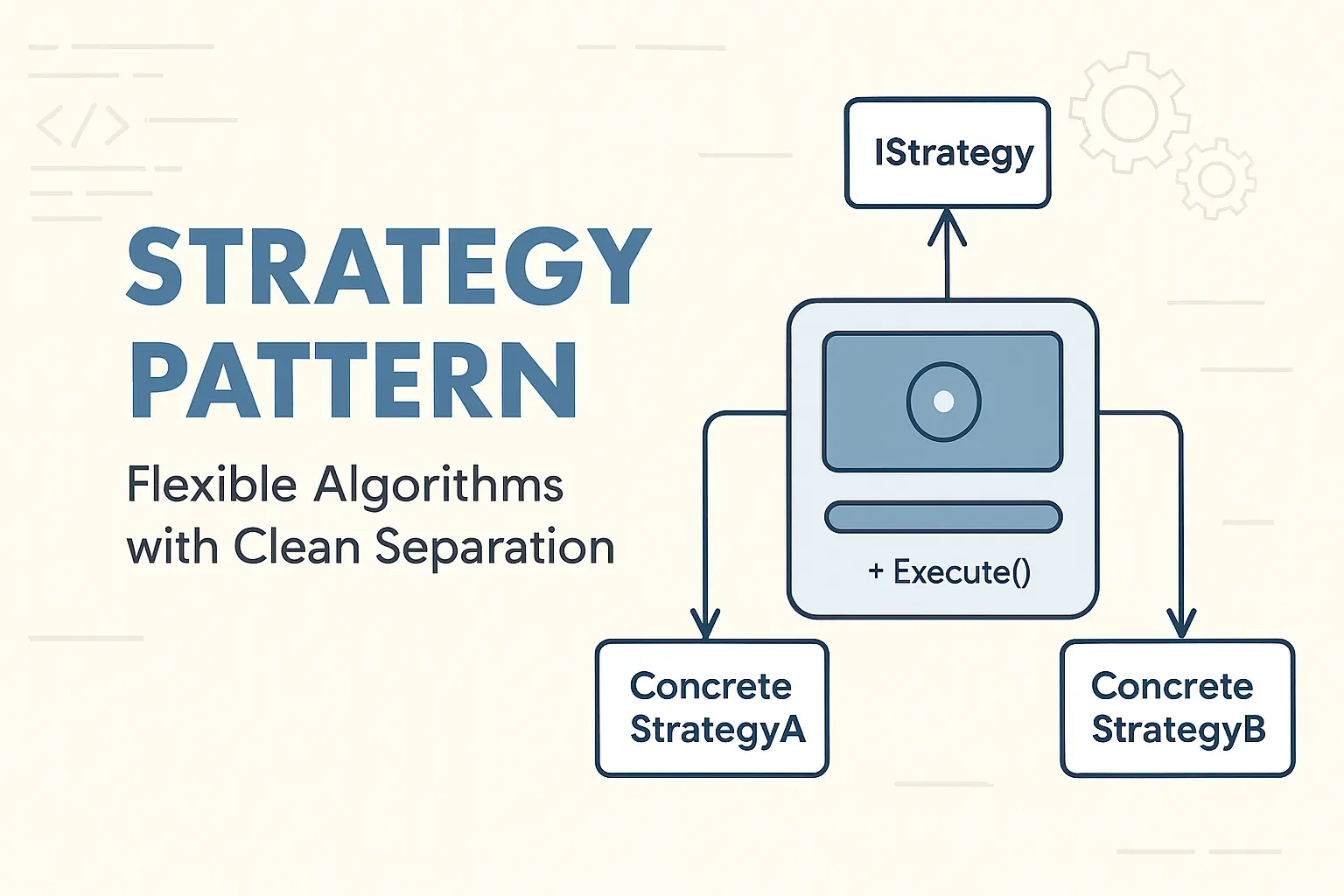
UML Diagram
Context → delegates to a Strategy interface, implemented by ConcreteStrategyA, ConcreteStrategyB
+----------------+ +---------------------+
| Context |<>----->| IStrategy |
|----------------| |---------------------|
| - strategy | | + Execute() |
|----------------| +---------------------+
| + SetStrategy()|
| + Execute() |
+----------------+
|
↓
+------------------+ +------------------+
|ConcreteStrategyA | |ConcreteStrategyB |
+------------------+ +------------------+
Code Example: Payment Strategy
// Strategy Interface
public interface IPaymentStrategy
{
void Pay(decimal amount);
}
// Concrete Strategy A
public class CreditCardPayment : IPaymentStrategy
{
public void Pay(decimal amount)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Paid {amount:C} using Credit Card.");
}
}
// Concrete Strategy B
public class PayPalPayment : IPaymentStrategy
{
public void Pay(decimal amount)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Paid {amount:C} using PayPal.");
}
}
// Context
public class PaymentProcessor
{
private IPaymentStrategy _paymentStrategy;
public void SetStrategy(IPaymentStrategy strategy)
{
_paymentStrategy = strategy;
}
public void ProcessPayment(decimal amount)
{
_paymentStrategy.Pay(amount);
}
}
// Client
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
var processor = new PaymentProcessor();
processor.SetStrategy(new CreditCardPayment());
processor.ProcessPayment(150.00m);
processor.SetStrategy(new PayPalPayment());
processor.ProcessPayment(200.00m);
}
}
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class PaymentStrategy(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def pay(self, amount):
pass
class CreditCardPayment(PaymentStrategy):
def pay(self, amount):
print(f"Paid ${amount:.2f} using Credit Card.")
class PayPalPayment(PaymentStrategy):
def pay(self, amount):
print(f"Paid ${amount:.2f} using PayPal.")
class PaymentProcessor:
def __init__(self, strategy: PaymentStrategy):
self._strategy = strategy
def set_strategy(self, strategy: PaymentStrategy):
self._strategy = strategy
def process_payment(self, amount):
self._strategy.pay(amount)
if __name__ == "__main__":
processor = PaymentProcessor(CreditCardPayment())
processor.process_payment(150.00)
processor.set_strategy(PayPalPayment())
processor.process_payment(200.00)
Code Example: Sorting Strategy
public interface ISortStrategy
{
void Sort(List list);
}
public class BubbleSort : ISortStrategy
{
public void Sort(List list)
{
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < list.Count - i - 1; j++)
{
if (list[j] > list[j + 1])
{
int temp = list[j];
list[j] = list[j + 1];
list[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Sorted using Bubble Sort: " + string.Join(", ", list));
}
}
public class QuickSort : ISortStrategy
{
public void Sort(List list)
{
list.Sort(); // Using built-in QuickSort
Console.WriteLine("Sorted using Quick Sort: " + string.Join(", ", list));
}
}
public class SortContext
{
private ISortStrategy _sortStrategy;
public void SetStrategy(ISortStrategy strategy)
{
_sortStrategy = strategy;
}
public void Sort(List list)
{
_sortStrategy.Sort(list);
}
}
public class SortExample
{
public static void Main()
{
var numbers = new List { 5, 3, 8, 4, 2 };
var context = new SortContext();
context.SetStrategy(new BubbleSort());
context.Sort(new List(numbers));
context.SetStrategy(new QuickSort());
context.Sort(new List(numbers));
}
}
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class SortStrategy(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def sort(self, data):
pass
class BubbleSort(SortStrategy):
def sort(self, data):
arr = data.copy()
for i in range(len(arr)):
for j in range(0, len(arr) - i - 1):
if arr[j] > arr[j + 1]:
arr[j], arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1], arr[j]
print("Sorted using Bubble Sort:", arr)
class QuickSort(SortStrategy):
def sort(self, data):
arr = sorted(data)
print("Sorted using Quick Sort:", arr)
class SortContext:
def __init__(self, strategy: SortStrategy):
self._strategy = strategy
def set_strategy(self, strategy: SortStrategy):
self._strategy = strategy
def sort(self, data):
self._strategy.sort(data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
numbers = [5, 3, 8, 4, 2]
context = SortContext(BubbleSort())
context.sort(numbers)
context.set_strategy(QuickSort())
context.sort(numbers)
More Real-World Examples
1. Compression Algorithm
You can use different strategies for compressing files such as ZIP, RAR, or GZIP.
2. Sorting
Context sets sorting strategy: QuickSort, MergeSort, or BubbleSort, depending on performance needs.
3. Authentication Strategy
Login context supports multiple strategies: LDAP, OAuth, SAML, or custom DB auth.
4. Logging Strategy
Log output can be directed to console, file, or cloud service via interchangeable strategies.
When to Use
- Multiple interchangeable algorithms
- Eliminating conditionals for algorithm selection
- Open/Closed Principle compliance
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Easy to switch strategies | Increased number of classes |
| Adheres to SOLID | Client must understand differences |
Real-World Use Cases
- Payment gateways
- Compression algorithms
- Input validation
- Sorting algorithms
- Authentication methods
- Logging destinations
Summary
The Strategy Pattern offers a powerful way to delegate and encapsulate behavior, making your code more flexible, extensible, and maintainable.